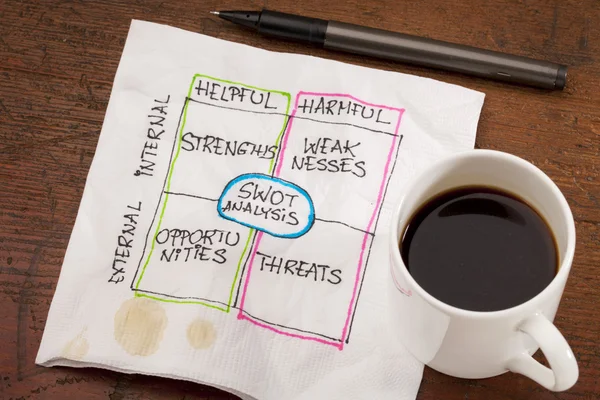
A SWOT Analysis is a strategic planning technique used by businesses, organizations, and individuals to identify and understand their Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. It serves as a foundation for making informed decisions and developing strategies to improve business performance or achieve specific goals. This article will dive into each component of the SWOT analysis and provide insights into how businesses can use it effectively.

What is SWOT Analysis?
SWOT stands for:
- Strengths
- Weaknesses
- Opportunities
- Threats
These four elements represent the internal and external factors that can influence a business’s success. SWOT analysis is a simple yet powerful tool that helps organizations analyze these factors to capitalize on strengths, mitigate weaknesses, seize opportunities, and minimize threats.
Internal Factors: Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths
Strengths are the internal capabilities and advantages a company possesses that give it a competitive edge in the marketplace. These could include unique products, strong brand recognition, skilled employees, financial stability, or efficient processes. Identifying strengths allows businesses to leverage these factors to achieve their objectives.
Examples of Strengths:
- Strong brand loyalty
- High customer satisfaction
- Patented technology or unique products
- Experienced leadership and talented staff
Weaknesses
Weaknesses are internal factors that hinder a company’s progress or place it at a disadvantage. Understanding weaknesses is essential to prevent them from becoming bigger problems in the future. Common weaknesses may include a lack of resources, outdated technology, or poor market presence.
Examples of Weaknesses:
- Limited financial resources
- Inefficient supply chain
- Poor brand recognition
- High employee turnover
External Factors: Opportunities and Threats
Opportunities
Opportunities refer to external factors that could help a company grow, improve, or expand. These may be market trends, technological advancements, changes in regulations, or new customer demands. Businesses must constantly monitor their environment to identify potential opportunities and act swiftly.
Examples of Opportunities:
- Emerging markets
- Changing customer preferences
- Technological advancements
- Government incentives
Threats
Threats are external factors that could harm or negatively impact a business. These could include increased competition, changing regulations, economic downturns, or supply chain disruptions. Identifying threats enables businesses to create contingency plans to minimize risk.
Examples of Threats:
- Rising competition
- Economic recession
- Changing regulations or trade policies
- Supply chain disruptions
Comparative SWOT Table
Below is a comparative table to summarize the four aspects of SWOT analysis:
| Aspect | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Strengths | Internal advantages that give the business a competitive edge | Strong brand, unique products, skilled workforce, advanced technology |
| Weaknesses | Internal limitations that hinder growth | Limited finances, outdated equipment, weak marketing presence |
| Opportunities | External factors that provide growth potential | Emerging markets, new customer trends, technological breakthroughs |
| Threats | External challenges that can negatively impact the business | Increased competition, economic instability, regulatory changes |
How to Conduct a SWOT Analysis
To conduct a SWOT analysis, follow these steps:
- Gather Data: Begin by collecting relevant information about your business, the industry, and the market. This can include financial reports, customer feedback, competitor analysis, and industry trends.
- Identify Strengths: List the internal factors that give your business a competitive advantage. Consider elements like expertise, resources, and customer loyalty.
- Pinpoint Weaknesses: Evaluate areas where your business is lacking. These could be inefficiencies, resource constraints, or internal challenges that need addressing.
- Spot Opportunities: Look for external factors that present growth potential. Think about emerging markets, new technologies, or regulatory changes that could be beneficial.
- Recognize Threats: Identify external risks that could harm your business. These could include new competitors, market shifts, or economic downturns.
- Analyze and Prioritize: Once you’ve completed the SWOT analysis, prioritize the factors based on their potential impact and develop strategies to build on strengths, address weaknesses, capitalize on opportunities, and mitigate threats.
How Businesses Can Use SWOT Analysis
SWOT analysis is a versatile tool that can be used for a variety of purposes, such as:
- Strategic Planning: Businesses can create long-term strategies by understanding their strengths and weaknesses and identifying opportunities for growth.
- Product Development: By recognizing market trends (opportunities) and potential competition (threats), companies can innovate their products to meet customer demands.
- Competitor Analysis: Comparing your business’s strengths and weaknesses against competitors can help you identify areas for improvement and competitive advantages.
- Risk Management: Identifying potential threats enables businesses to develop contingency plans and minimize risks.
A SWOT analysis is an essential tool for businesses looking to understand their position in the marketplace and develop strategies for success. By evaluating internal strengths and weaknesses and analyzing external opportunities and threats, companies can make informed decisions and stay competitive. Incorporating SWOT analysis into regular strategic planning ensures that businesses remain proactive in the ever-changing business environment.





